5 Parallelism
Basics
Amdahl’s Law

Speedup =
F = Fraction of execution time speed up
S = Scale of improvement
SIMD
SIMD Architecture
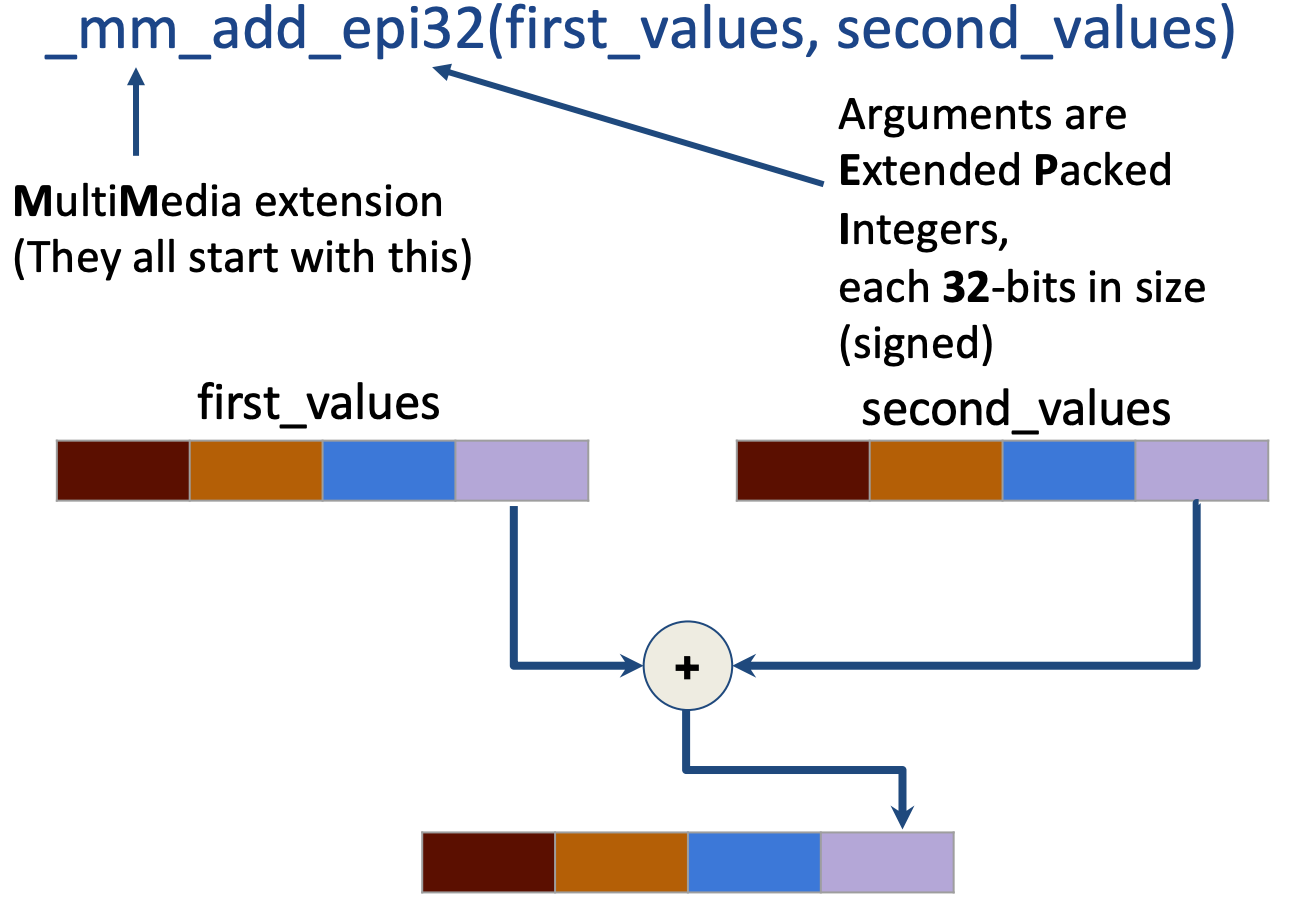
X86 Intrinsics AVX Data Type

Intrinsics AVX Code nomenclature [ˈnomənˌkletʃɚ]name call

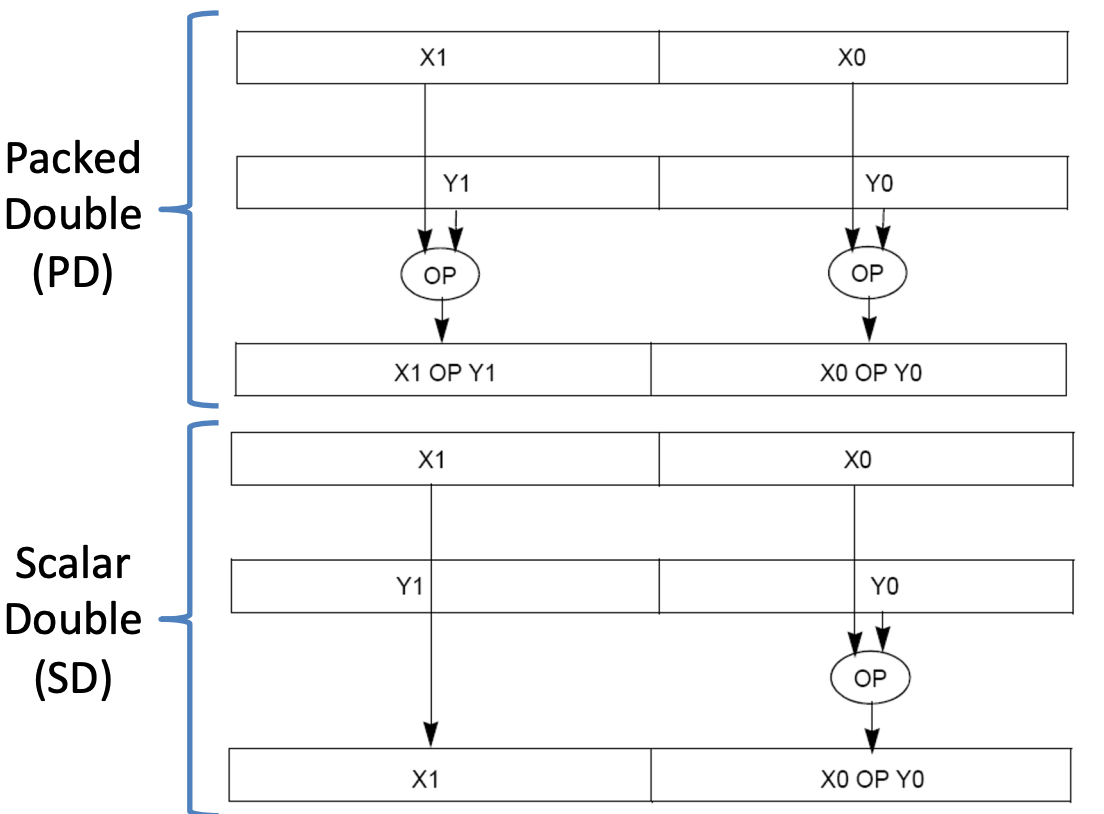
Example
Loop Unrolling
Loop Unrolling in C
for(i=0; i<1000; i++)
x[i] = x[i] + s;
//Unrolling
for(i=0; i<1000; i=i+4) {
x[i] = x[i] + s;
x[i+1] = x[i+1] + s;
x[i+2] = x[i+2] + s;
x[i+3] = x[i+3] + s;
}
RISCV
Loop:
lw t0, 0(s0)
addu t0,t0,s1 # add b to array element
sw t0,0(s0) # store result
addi s0,s0,4 # move to next element
bne s0,s2,Loop # repeat Loop if not done
Unrolling Loop:
lw t0,0(s0)
lw t1,4(s0)
lw t2,8(s0)
lw t3,12(s0) # 4 wide SIMD Load
add t0,t0,s1
add t1,t1,s1
add t2,t2,s1
add t3,t3,s1 # 4 wide SIMD Add
sw t0,0(s0)
sw t1,4(s0)
sw t2,8(s0)
sw t3,12(s0) # 4 wide SIMD Store
addi s0,s0,16
bne s0,s2,Loop
Matrix Multiply
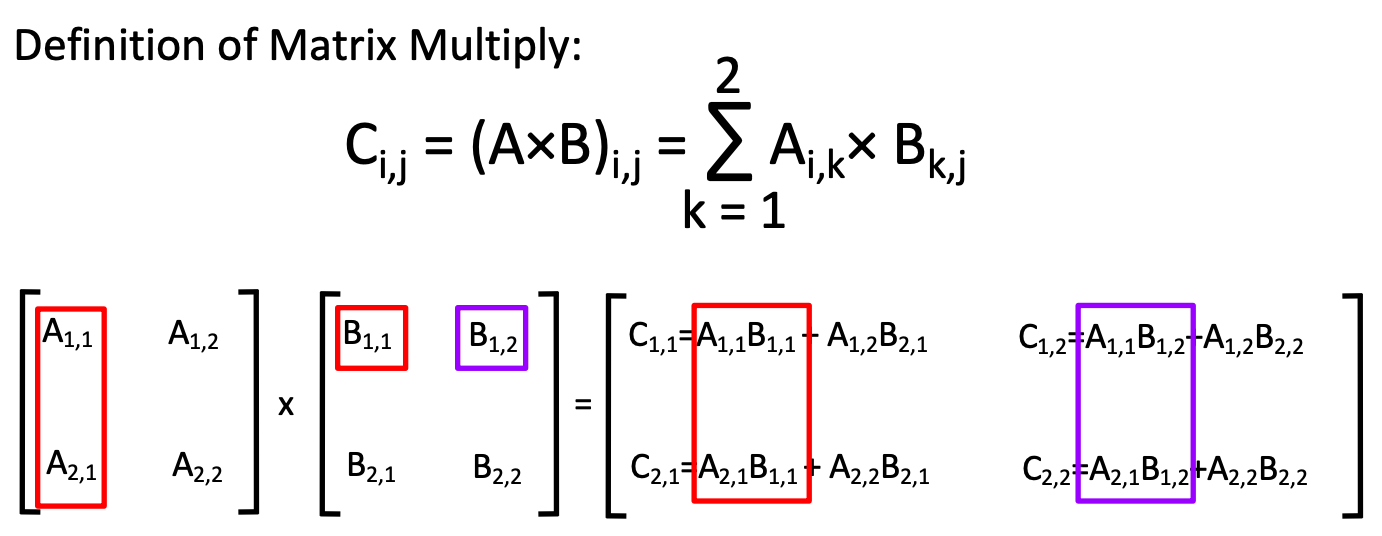
Now, i、j、k are N, we divide i by 4 each block.
so C[i][j] whole row can be divided by 4, each column entry(j) can be divided by N(k)
#include <x86intrin.h>
void mm_scalar(int N, double *a, double *b, double *c) {
for(int i=0;i<N;i+=4){
for(int j=0;j<N;++j){
__m256d c0 = {0,0,0,0};
for (k = 0; k < N; k++) {
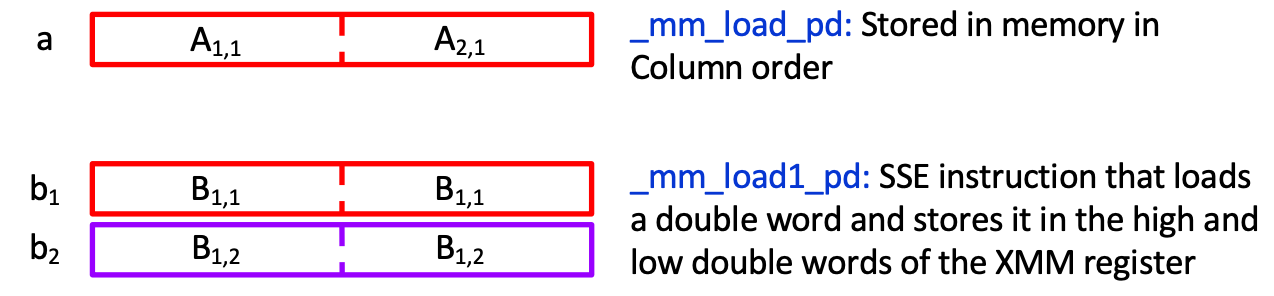
c0 = _mm_add_pd(c0,_mm_mul_pd(_mm_load_pd(a+i+k*N),_mm_load1_pd(b+k+j*N)))
//c0 += a[i][k] * b[k][j]
}
_mm_store_pd(c+i+j*N,c0);
}
}
return 0;
}
const int UNROLL = 4;
// Unrolling
void mm_unroll(int N, double *A, double *B, double *C) {
for (int i=0; i<n; i+= UNROLL*4) {
for (int j=0; j<n; j++) {
__m256d c[4];
for (int x=0; x<UNROLL; x++)
c[x] = _mm_load_pd(C+i+x*4+j*N);
for (int k=0; k<n; k++) {
__m256d b = _mm_load1_pd(B+k+j*n);
for (int x=0; x<UNROLL; x++)
c[x] = _mm_add_pd(c[x],
_mm_mul_pd(_mm_load_pd(A+i+x*4+k*N), b));
}
for (int x=0; x<UNROLL; x++)
_mm_store_pd(C+i+x*4+j*N, c[x]);
}
}
}
// Cache Blocking
const int BLOCKSIZE = 32;
void do_block(int n, int si, int sj, int sk, double *A, double *B, double *C) {
for (int i=si; i<si+BLOCKSIZE; i+=UNROLL*4)
for (int j=sj; j<sj+BLOCKSIZE; j++) {
__m256d c[4];
for (int x=0; x<UNROLL; x++)
c[x] = _mm_load_pd(C+i+x*4+j*N);
for (int k=sk; k<sk+BLOCKSIZE; k++) {
__m256d b = _mm_load1_pd(B+k+j*n);
for (int x=0; x<UNROLL; x++)
c[x] = _mm_add_pd(c[x],
_mm_mul_pd(_mm_load_pd(A+i+x*4+k*N), b));
}
for (int x=0; x<UNROLL; x++)
_mm_store_pd(C+i+x*4+j*N, c[x]);
}
}
void mm_block(int n, double* A, double* B, double* C) {
for(int sj=0; sj<n; sj+=BLOCKSIZE)
for(int si=0; si<n; si+=BLOCKSIZE)
for (int sk=0; sk<n; sk += BLOCKSIZE)
do_block(n, si, sj, sk, A, B, C);
}
MIMD
OpenMP
Synchronization
Reduction: specifies that 1 or more variables that are private to each thread are subject of reduction operation at end of parallel region
double compute_sum(double *a, int a_len) {
double sum = 0.0;
#pragma omp parallel for reduction(+ : sum)
for (int i = 0; i < a_len; i++) {
sum += a[i];
}
return sum;
}
Pitfalls
Data dependencies
a[0] = 1;
for(i=1; i<5000; i++)
a[i] = i + a[i-1];Sharing Issues
// Problem
#pragma omp parallel for //Each thread accesses different elements of a, b,and c, but the same temp
for(i=0; i<n; i++){
temp = 2.0*a[i];
a[i] = temp;
b[i] = c[i]/temp;
}
// Correct
#pragma omp parallel for private(temp)
for(i=0; i<n; i++){
temp = 2.0*a[i];
a[i] = temp;
b[i] = c[i]/temp;
}Updating Shared Variables Simultaneously
This can be done by surrounding the summation by a critical/atomic section or reduction clause
Parallel Overhead
Parallelize over the largest loop that you can (even though it will involve more work to declare all of the private variables and eliminate dependencies)