1 Class
Data Types
Primitive Data Types
C++(ILP32:int long pointer)
| Type | Storage(bits) |
|---|---|
| char | 8 |
| short | 16 |
| int | 32 |
| long | 32 |
| float | 32 |
| long long | 64 |
| double | 64 |
Java
| Type | Storage(bits) | Min Value | Max Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| boolean | - | - | - |
| byte | 8 | -128 | 127 |
| short | 16 | ||
| char | 16 | 0 | |
| int | 32 | ||
| long | 64 | ||
| float | 32 | Approximately-3.4e+38 with 7 significant digits | Approximately3.4e+38 with 7 significant digits |
| double | 64 | Approximately-1.7e+308 with 15 significant digits | Approximately-1.7e+308 with 15 significant digits |
Operator precedence
单算移关与,异或逻条赋
- 单表示单目运算符:逻辑非(!),按位取反(~),自增(++),自减(--),取地址(&),取值(*)
- 算表示算术运算符:乘、除和求余(*,/,%)级别高于加减(+,-)
- 移表示按位左移(<<)和位右移(>>)
- 关表示关系运算符:大小关系(>,>=,<,<=)级别高于相等不相等关系(==,!=)
- 与表示按位与(&)
- 异表示按位异或(^)
- 或表示按位或(|)
- 逻表示逻辑运算符:逻辑与(&&)级别高于逻辑或(||)
- 条表示条件运算符(? :)
- 赋表示赋值运算符(=,+=,-=,*=,/=,%=,>>=,<<=,&=,^=, |=,!=)
Immutability: final
- Primitive types ensure immutability
- Declaring a reference as final does not make object immutable
Initialization
- Data Field
- null for a reference type
- 0 for a numeric type
- false for a boolean type
- '\u0000' for a char type
- no default value to a local variable
Pass by value
- For a parameter of a primitive type, the actual value is passed
- For a parameter of an array type, the reference value is passed
Object
| Function | Interpretion |
|---|---|
| boolean equals(Object w) | 判断两个对象变量是否指向同一个对象 |
| String toString() | Returns a string representation of the object. |
| Class<?>getClass() | Returns the runtime class of this Object. |
| protected Object clone() | Creates and returns a copy of this object. |
| int hashCode() |
Autoboxing(auto-unboxing)
Implicit conversions between wrapper/primitives.
public class BasicArrayList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> L = new ArrayList<Integer>();
L.add(5);
L.add(6);
int first = L.get(0);
}
}
Arrays are never autoboxed/unboxed, e.g. an Integer[] cannot be used in place of an int[] (or vice versa).
Object Comparison
public interface Comparable<T> {
public int compareTo(T obj);
}
public interface Comparator<T> {
int compare(T o1, T o2);
}
public class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
private String mSurname;
private int mAge;
public int compareTo(Person p) {
return mSurname.compareTo(p.mSurname);
}
}
public class AgeComparator implements Comparator<Person> {
public int compare(Person p1, Person p2) {
return (p1.mAge-p2.mAge);
}
}
ArrayList<Person> plist = ...;
// 法1: sorts by surname
Collections.sort(plist);
// 法2: sorts by age
// Collections.sort(plist, new AgeComparator());
Designing Classes
Constructor
- Constructors must have the same name as the class itself
- A constructor with no parameters is referred to as a no-arg constructor(default: no-arg constructor with an empty body)
- Constructors do not have a return type(Not even void)
POJO: plain old java object, sometimes called an Entity
DTO: data transfer object
Visibility Modifiers
Class level: Only public and (default)
Member level:
| Modifiers | Description |
|---|---|
| public | The member is visible to any class in any package |
| protected | default + inheritance |
| (default) | By any class in the same package (aka package private) |
| private | Only by the declaring class |
//package a;
public class Vehicle {
protected void drive() {System.out.print("Drive !");}
void stop() {System.out.print("Stop !");}
}
// package b
// import a.Vehicle;
public class Car extends Vehicle {
private void test(Vehicle obj) {
obj.drive();// invisible to different package
drive(); // compile ok
stop(); // invisible to different package
}
}
Class Import
- The normal import declaration imports classes from packages, allowing them to be used without package qualification
- The static import declaration imports static members from classes, allowing them to be used without class qualification
- Common Scenario: local copies of constants
import static java.lang.Math.cos;
double r = cos(PI * theta);
Order of Initialization
1.Staic members is to be initialized in the loading of the class,属于类的数据(C++全局)
2.When a new object is create,顺序:
- Allocate enough storage for an object on the heap.
- Setting all the primitives in the object to their default values.(Any initializations that occur at the point of field definition are executed.)
- Constructors are executed.
Cleanup:finalize()
When the garbage collector is ready to release the storage used for your object,it will first call its finalize() to clean up temporary files, close sockets/connections, etc.
- Blocking: pause the program when collecting garbage
- Incremental: collect in multiple phases and let the program run in the gaps
- Concurrent: runs concurrently with the program
Compare with C++:
void UseRawPointer()
{
MyClass *mc = new MyClass();
delete mc;//manually deleted
}// or auto-deleted when out of scope
Problems:
We either forget to delete (memory leak) or we delete multiple times (crash)
Inheritance & Polymorphism
Inheritance
private、static method cannot be overriden
If a static method defined in the superclass is redefined in a subclass, the method defined in the superclass is hidden
// 区分instance 和 static method
public class BaseClass
{
public void objectAction();
public static void classAction()
{
System.out.println("classAction in BaseClass.");
}
}
public class DerivedClass extends BaseClass
{
public void objectAction()
{
this.classAction(); // OK
}
public static void classAction()
{
//super.objectAction(); // Not OK
BaseClass.baseAction();// OK
}
}
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
DerivedClass derivedObject = new DerivedClass();
BaseClass baseObjectAlias = derivedObject;
baseObjectAlias.classAction();//classAction in BaseClass. Hide but not override
}
Overriding
- Have the same signature
- Are in different classes related by inheritance
Overloading
- Have the same name, but different parameter lists
- Can be either
- In the same class
- In different classes related by inheritance
Eg:
System.out.println(true?Integer.valueOf(1):Double.valueOf(2))
//输出1.0,因为java是编译语言不是解释语言,编译器看到函数调用不会立即执行
//而是根据double确定println overload为double类型
Polymorphism
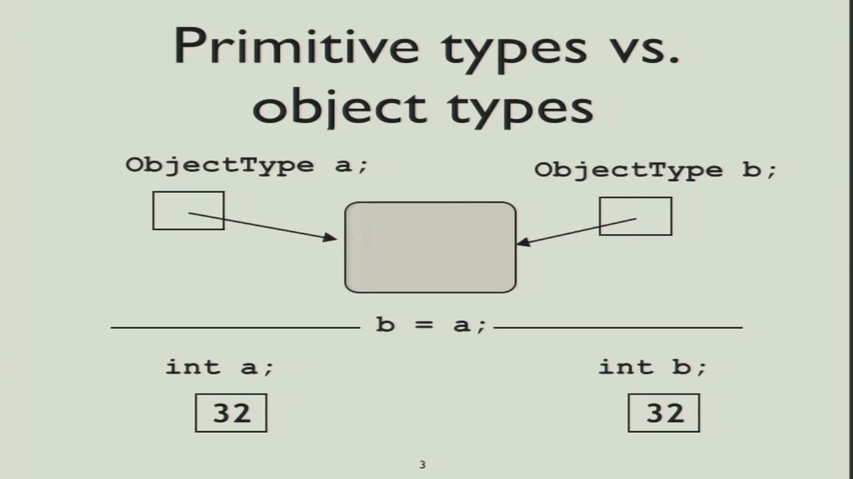
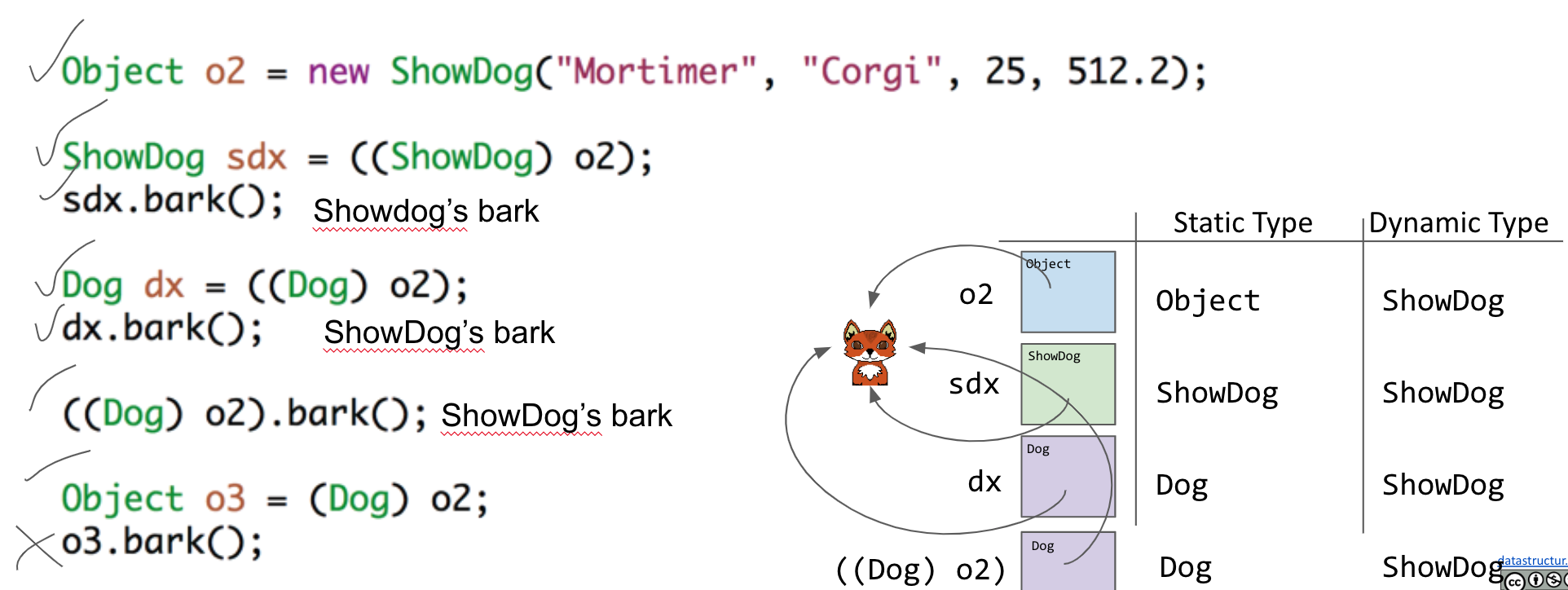
The compiler chooses the most specific matching method signature from the static type of the invoking class
- Static Type: type specified at declaration
- Dynamic Type: type specified at instantiation(the object being pointed at)
- dynamic method selection: if dynamic type overides the method, its method is used instead.
Casting Problem:
- Compiler allows method calls based on compile-time(static) type of variable
- (联想集合)To move from a wider type to a narrower type, must use casting
Abstract Classes & Interfaces
One can implement multiple interfaces, but extend only one class:
multiple interface inheritance, but single body inheritance.
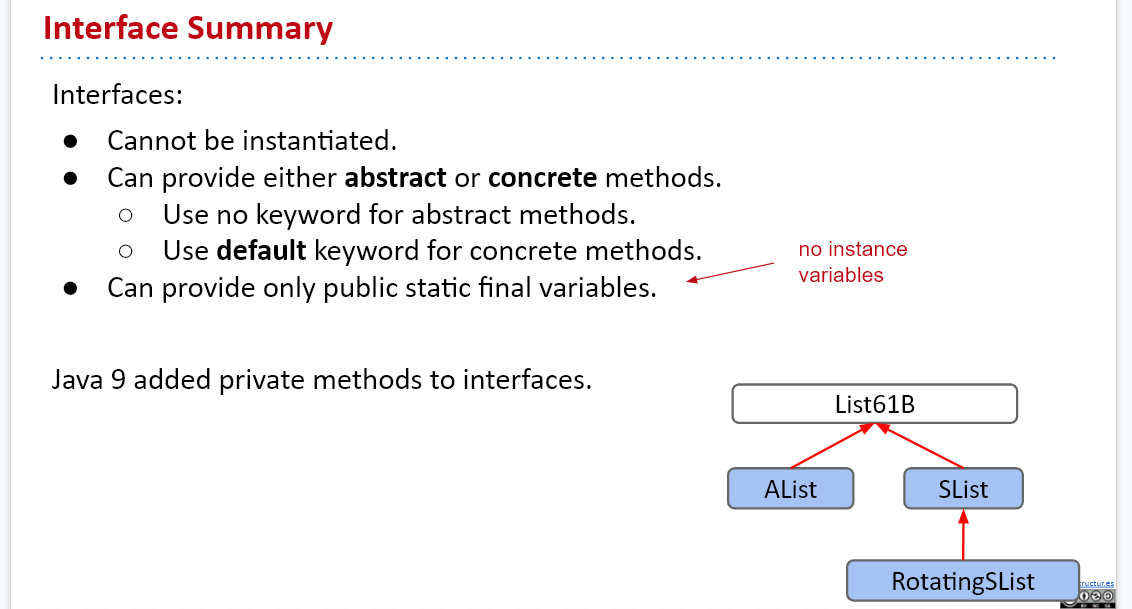
Interfaces
Interfaces may combine a mix of abstract and default methods.
- Unless you use the keyword default, a method will be abstract
- Unless you specify an access modifier, a method will be public(All method declarations in an interface, including default methods, are implicitly public, so you can omit the public modifier.)
- Can provide variables, but they are public static final
public interface Module {
double gravity = 6.67e-11;
void update(double dt);
public default void doSomething() {
System.out.println("Do something");
}
}
// Interface as a data type
Module[] instances = new Module[1];
instances[0] = new module{
void update(double dt){}
}
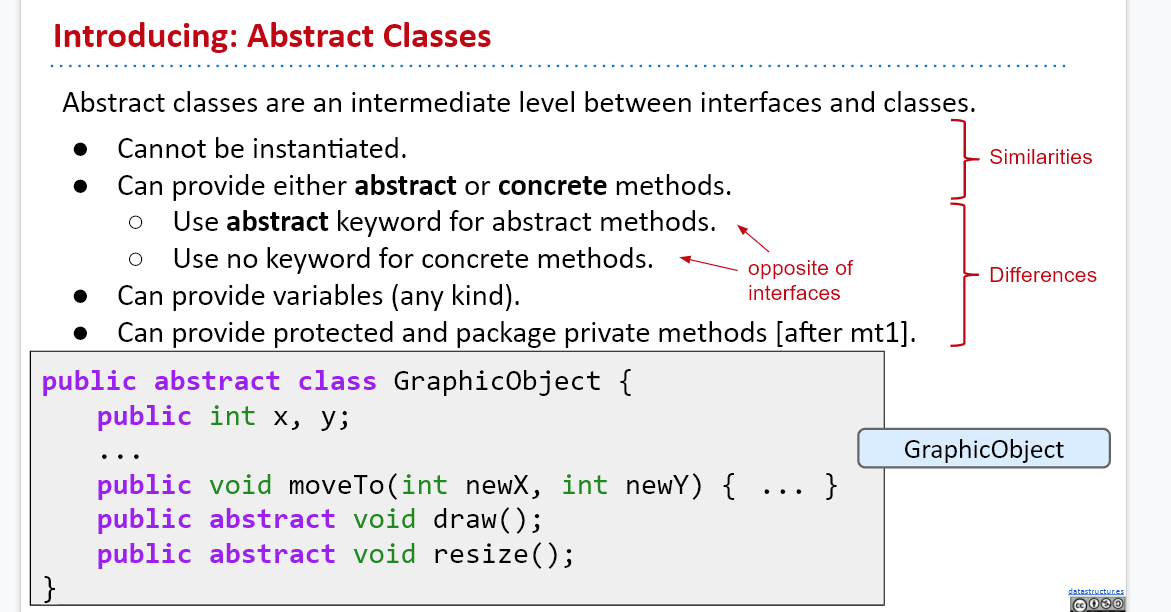
Abstract Class
Abstract method(only a signature without implementation)
Abstract class as a data type
GeometricObject[] objects = new GeometricObject[2];
Anonymous Class
R = map(new IntUnaryFunction() {
public int apply(int x) {
return Math.abs(x);
}
}, some list);
//Equals to
class Anonymous implements IntUnaryFunction {
public int apply(int x) {
return Math.abs(x);
}
}
R = map(new Anonymous(), some list);
Lambda Expression
- A comma-separated list of formal parameters enclosed in parentheses(Optional type declaration)
- The arrow token, ->
- A body, which consists of a single expression or a statement block.
//一个参数时()可省略
(param1, param2, …, paramN) -> { statements }
(param1, param2, …, paramN) -> expression
//相当于:(param1, param2, …, paramN) ->{ return expression; }
// Anonymous 可以改写
R = map((int x) -> Math.abs(x), some list);
// or even better, Method Reference
R = map(Math::abs, some list);
Method Reference
- Reference to a static method
- ContainingClass::staticMethodName
- Reference to an instance method of a particular object
- containingObject::instanceMethodName
- Reference to an instance method of an arbitrary object of a particular type
- String::concat
- Reference to a constructor
- HashSet::new
Other Classes
java.util.Scanner
Class Scanner implements Iterator<String>, Closeable{
Scanner(InputStream source);
// move forward one byte/int, return the one scanned from the input
// hasnextByte()/nextByte()
// hasnextShort()/nextShort()
// hasnextInt()/nextInt()
// hasnextLine()/nextLine(), returns the rest of the current line, excluding any line separator at the end
}
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int value = input.nextInt();
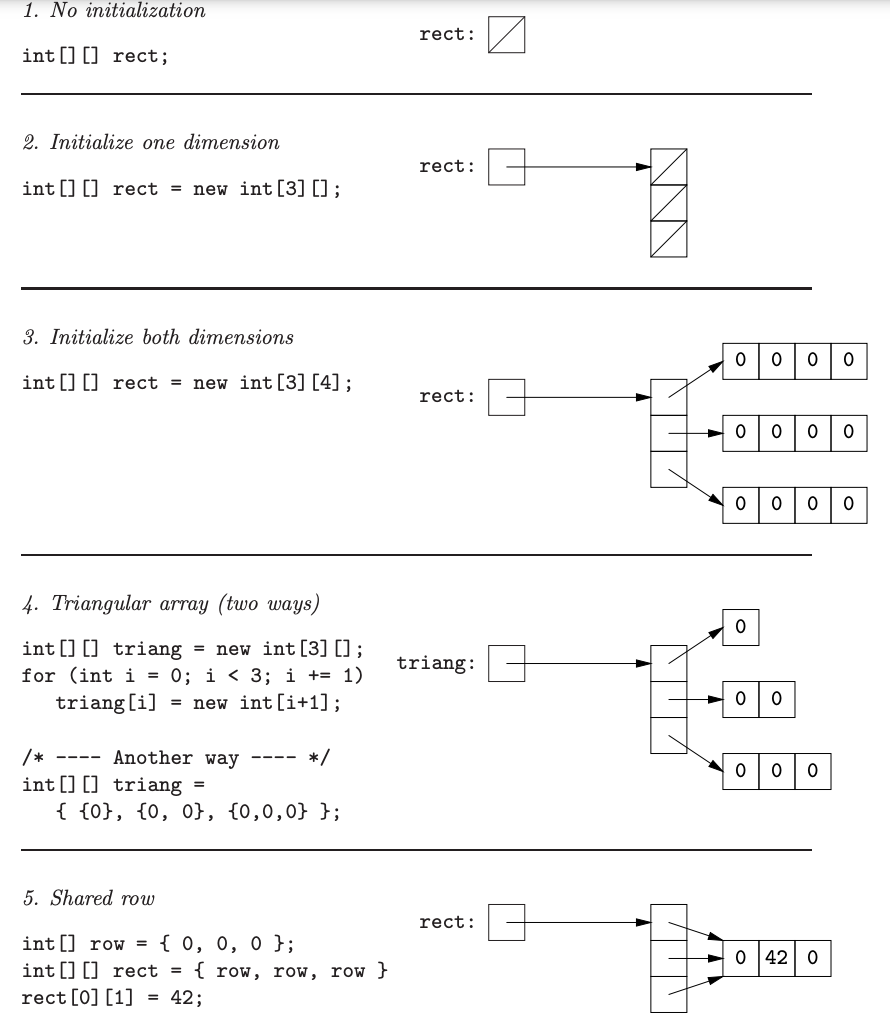
java.util.Arrays
get length: (Object you create).length
/***Creation****/
int[] A = new int[4]; // A points to array of 4 0s.
int[] B; // Same thing, but in two steps.
B = new int[4];
int[] C = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 }// Array with explicit initial values.
int[] D = { 1, 2, 3, 4 } // Shorthand for the above
/***Method******/
public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a)//Returns a fixed-size list backed by the specified array.
public static <T> void sort(T[] a,
int fromIndex,
int toIndex,
Comparator<? super T> c)
public static boolean equals(Object[] a,
Object[] a2)//Returns true if the two specified arrays of Objects are equal to one another.
public static void fill(Object[] a,
int fromIndex,
int toIndex,
Object val)
java.lang.String
//Can't modify
Class String{
char charAt(int index);
String concat(String s1); // Returns a new string that concatenates this string with string s1.
static String format(String format, Object... args);
String formatted(Object... args);
boolean isEmpty();
int indexOf(String str);
int length();
String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex);
String toUpperCase();//Returns a new string with all letters in uppercase
String toLowerCase();
String trim();//Returns a string whose value is this string, with any leading and trailing whitespace removed.
}
// Can modify
Class StringBuilder implements CharSequence{
StringBuilder(int capacity);
StringBuilder(CharSequence seq);//Constructs a string builder that contains the same characters as the specified CharSequence
StringBuilder(String str);//Constructs a string builder initialized to the contents of the specified string
StringBuilder append(String s);// 会变
StringBuilder append(char c);// 会变
StringBuilder append(CharSequence s);// 会变
char charAt(int index);
int length();
void setCharAt(int index, char ch);
StringBuilder reverse();
}
int age = 12;
String formattedString = "Your age is %d".formatted(age);
String formattedString = String.format("Your age is %d",age);
// ParseInt
String ageStr = "13";
age = Integer.parseInt(ageStr);