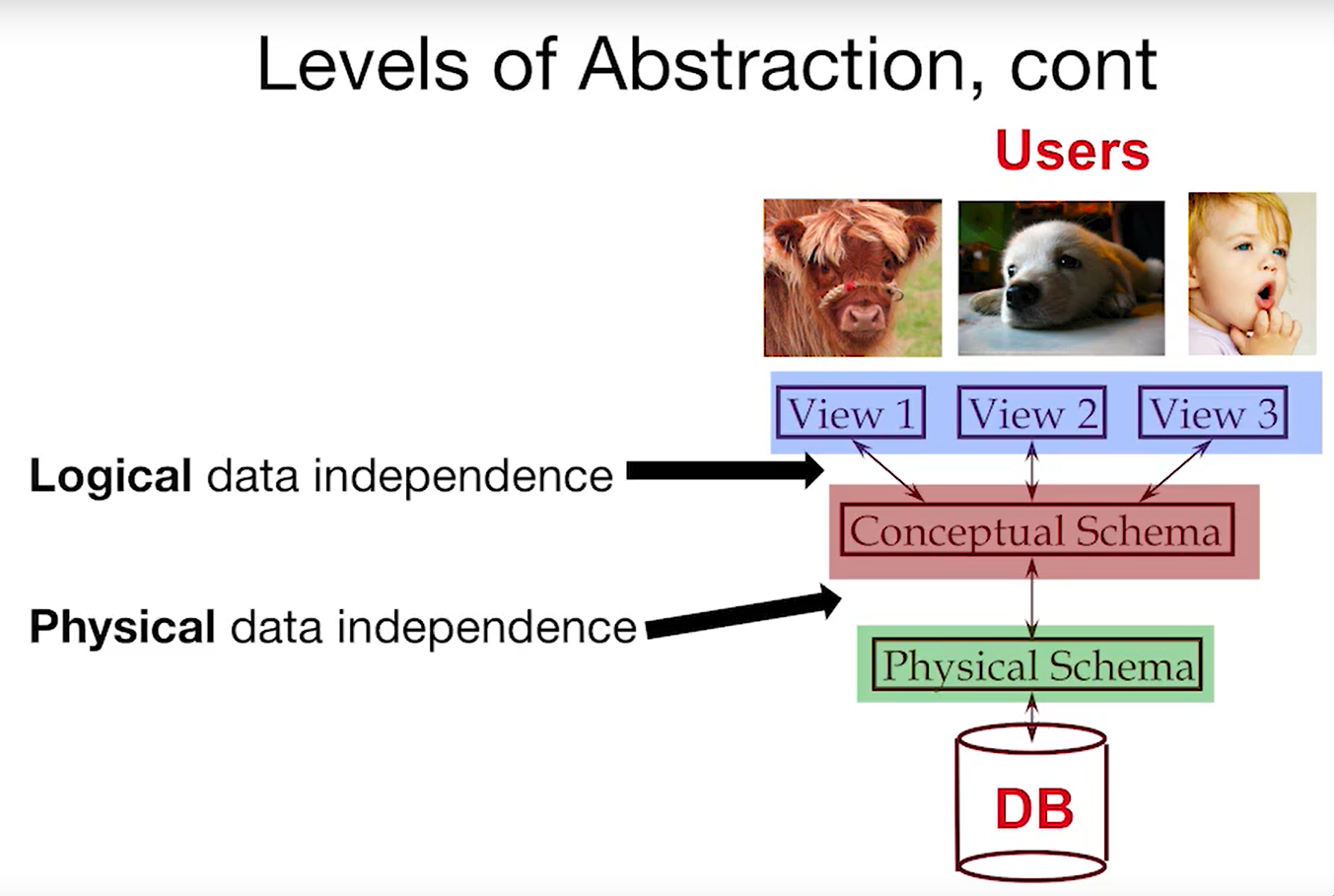
2 Data Models
Logical data independence: Maintain views when logical structure changes
Phisical data independence: Maintain logical structure when phisical structure changes
ER Model
Key constraints
arrow: 可以divided(从尾到头at most one)
graph RL
id1[Departments]-->id2{Manages};
subgraph 1
*did*---id1;
dname---id1;
budget---id1;
end
id2---id3[Employees];
subgraph 2
*ssn*---id3;
name---id3;
lot---id3;
end
create table manages(
ssn char(11),
did integer,
primary key (did),
foreign key (ssn) references Employees,
foreign key (did) references Departments
)
Participation constraints
粗线: Total participation(从尾到头at least one)
故以下从尾到头exactly one
graph RL
id1[Departments]==>id2{Manages};
subgraph 1
*did*---id1;
dname---id1;
budget---id1;
end
id2---id3[Employees];
subgraph 2
*ssn*---id3;
name---id3;
lot---id3;
end
create table manages(
did integer,
dname char(20),
budget real,
ssn char(11) not null,
primary key(did),
foreign key (ssn) references Employees on delete no action
)
Weak Entity Set
An entity set that does not have a primary key
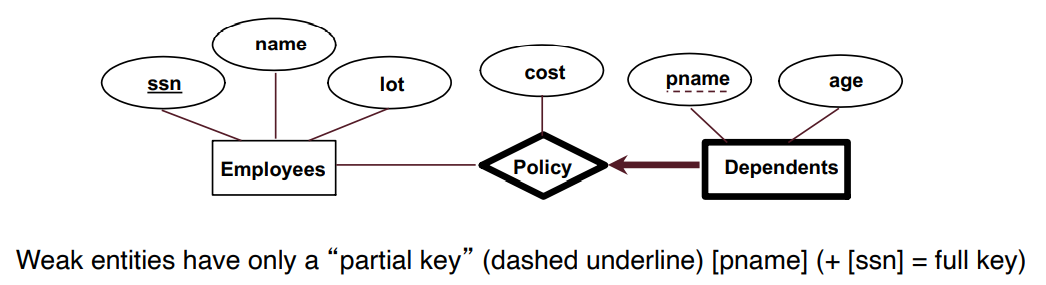
create table Dep_Policy(
pname char(20),
age integer,
cost real,
ssn char(11) not null,
primary key (pname,ssn),
foreign key (ssn) references employees on delete cascade
)
Functional Dependencies
Definition
Let be a relation scheme
let and .
We say that a relation instance satisfies a functional dependency if for every pair of tuples and , if then .
ArmStrong's Axioms
Reflexivity: If , then (trivial FD)
Augmentation: If , then for any Z.
Transitivity: If and , then
Union: If and , then
Decomposition: If , then and
Keys
A superkey is a set of attributes s.t.
for any other attribute B, we have
A candidate key (or sometimes just key) is a minimal superkey