6 Web Frameworks and ORM
Spring
@Bean
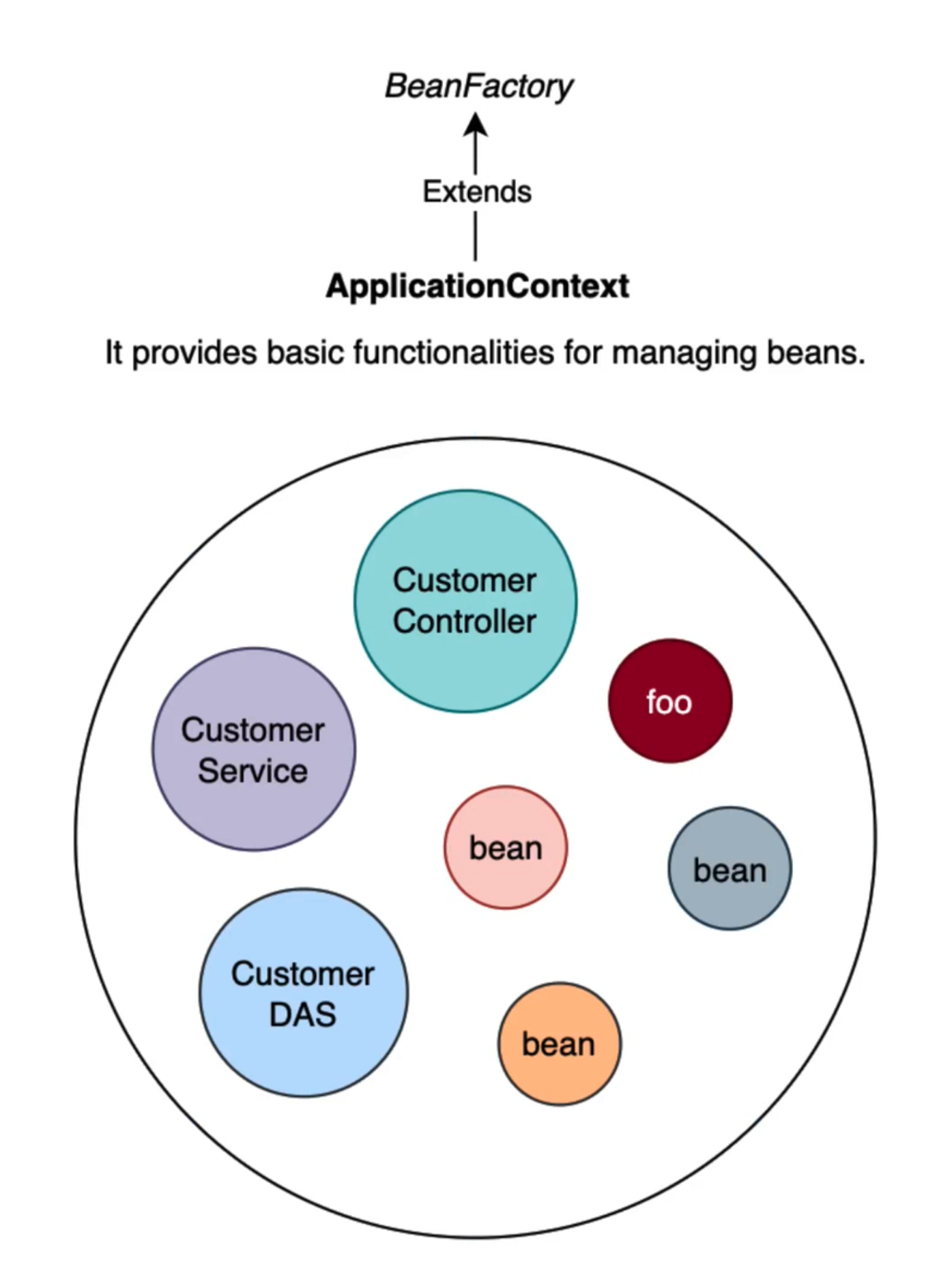
Each component in your Spring application is called a Bean. A class is annotated as being such with @bean, or another annotation wihch inherits from it. This is what tells the IOC/DI system inside Spring to treat the class as a component within the system.
@Component
This annotation tells spring that this class is a component and should be managed by the spring container.
@Configuration
Configuration classes are used to create beans, convetionally called AppConfig. if you want to have a bean dependent on another bean you must define it inside of a configuration class.
@Service
Service, unlike the other types of component offers no special functionality over @Component and is instead merely used to further show the intent of the class.
Springboot
@SpringBootApplication
@SpringBootApplication = @Configuration + @EnableAutoConfiguration + @ComponentScan
@EnableAutoConfiguration
It makes Spring guess the configuration based on the JAR files available on the classpath. It can figure out what libraries you use and pre-configure their components without you lifting a finger.
SpringWebMVC
@Controller
@Controller marks the class as a web controller.
@RestController
@RestController = @Controller + @ResponseBody
@ResponseBody
The @ResponseBody is a utility annotation that tells Spring to automatically serialize return values of this classes methods into HTTP responses.
When building a JSON endpoint, this is an amazing way to "magically" convert your objects into JSON for easier consumption.
ORM
- ORM: Object Relational Mapping
- JPA: Jakarta Persistence API is a Jakarta EE application programming interface that describes the management of relational data in enterprise Java applications