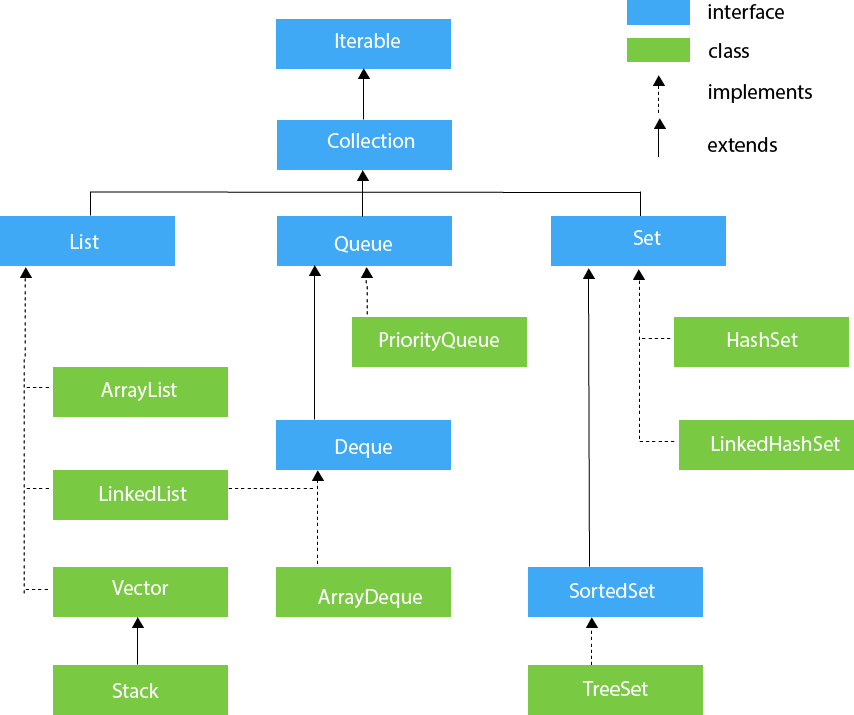
2 Collection
Collection
Interface Iterable<T>{
default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action)//Performs the given action for each element of the Iterable until all elements have been processed or the action throws an exception.
Iterator<T> iterator()//Returns an iterator over elements of type T.
}
public interface Iterator<E>{
boolean hasNext();
E next();//Returns the next element in the iteration.
}
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E>{
int size();
boolean add(E e);
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);
void clear();
boolean contains(Object);
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean isEmpty();
default Stream<E> stream();//Returns a sequential Stream with this collection as its source.
default Stream<E> parallelStream();//Returns a possibly parallel Stream with this collection as its source.
boolean remove(Object o);
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);//Retains only the elements in this collection that are contained in the specified collection
Object[] toArray();//Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection.
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);
}
Consumer Inferface
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Consumer<T>{
void accept(T t);
}
List
- ArrayList: implement with an array, slow for inserting and removing.
- LinkedList: inexpensive insertions and deletions, slow for random access.
- LinkedList is a doubly-linked list implementation of the List and Deque interfaces
Interface List<E>{
E get(int index);
int indexOf(Object o);
int lastindexOf(Object o);
static <E> List<E> of(E... elements);
E set(int index, E element);// returns the element previously at the specified position
Object[] toArray();
}
Queue
- Queues typically, but do not necessarily, order elements in a FIFO manner
- The head of the queue is that element which would be removed by a call to remove() or poll()
- In a FIFO queue, all new elements are inserted at the tail of the queue
Queue methods:
| Name | Throws exception | Returns special value |
|---|---|---|
| Insert | add(e) | offer(e) |
| Remove | remove() | poll() |
| Examine | element() | peek() |
Deque[dek]--double ended queue
| Name | First Element (Head) | Last Element (Tail) |
|---|---|---|
| Insert | addFirst(e) | addLast(e) |
| Remove | removeFirst() | removeLast() |
| Examine | getFirst() | getLast() |
Set
- HashSet: Objects must also define hashCode()
- TreeSet: An ordered Set backed by a tree.
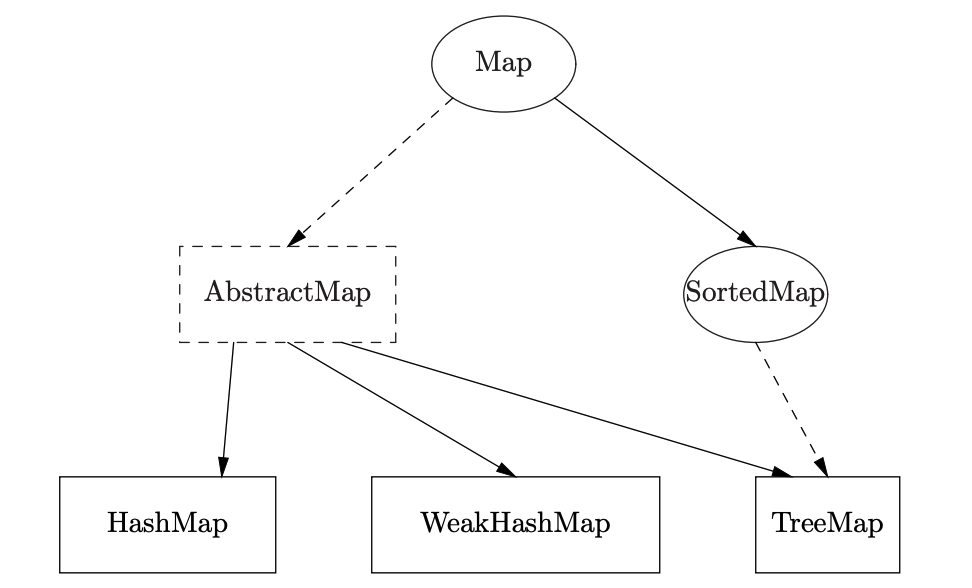
Map
public interface Map<K,V>{
int size();
void clear();
boolean containsKey(Object key);
boolean containsValue(Object value);
default void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K,? super V> action);
V put(K key,V value)//Returns the previous value associated with key, or null if there was no mapping for key.
V get(Object key);//Returns the value or null
boolean isEmpty();
V remove(Object key);
default V replace(K key, V value);
Collection<V> values();
}
Collections
public class Collections extends Object{
static <T> void fill(List<? super T> list, T obj);//Replaces all of the elements of the specified list with the specified element.
static <T> T max(Collection<? extends T> coll,Comparator<? super T> comp);
static <T> T min(Collection<? extends T> coll,Comparator<? super T> comp);
static void reverse(List<?> list);
static <T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c);
static void swap(List<?> list, int i, int j);
}
Generics
无论是什么泛型,getClass()均是同一个
机制
Java--类型参数(Cannot use primitive types)作为类的成员变量
C++(模板)--源代码的源代码
The most commonly used type parameter names are:
- E: Element
- K: Key
- N: Number
- T: Type
- V: Value
Class
public class ArrayMap<K, V> {
private K[] keys;
private V[] values;
private int size;
public ArrayMap() {
keys = (K[]) new Object[100];
values = (V[]) new Object[100];
size = 0;
}
public void put(K key, V value) {
int i = getKeyIndex(key);
if (i > -1) {
values[i] = value; return; }
keys[size] = key;
values[size] = value;
size += 1;
}
public V get(K key) {
return values[findKey(key)];
}
public static void main(String[] args){
ArrayMap<Integer, String> ismap = new ArrayMap<Integer, String>();
ismap.put(5, "hello");
ismap.put(10, "ketchup");
}
}
Method
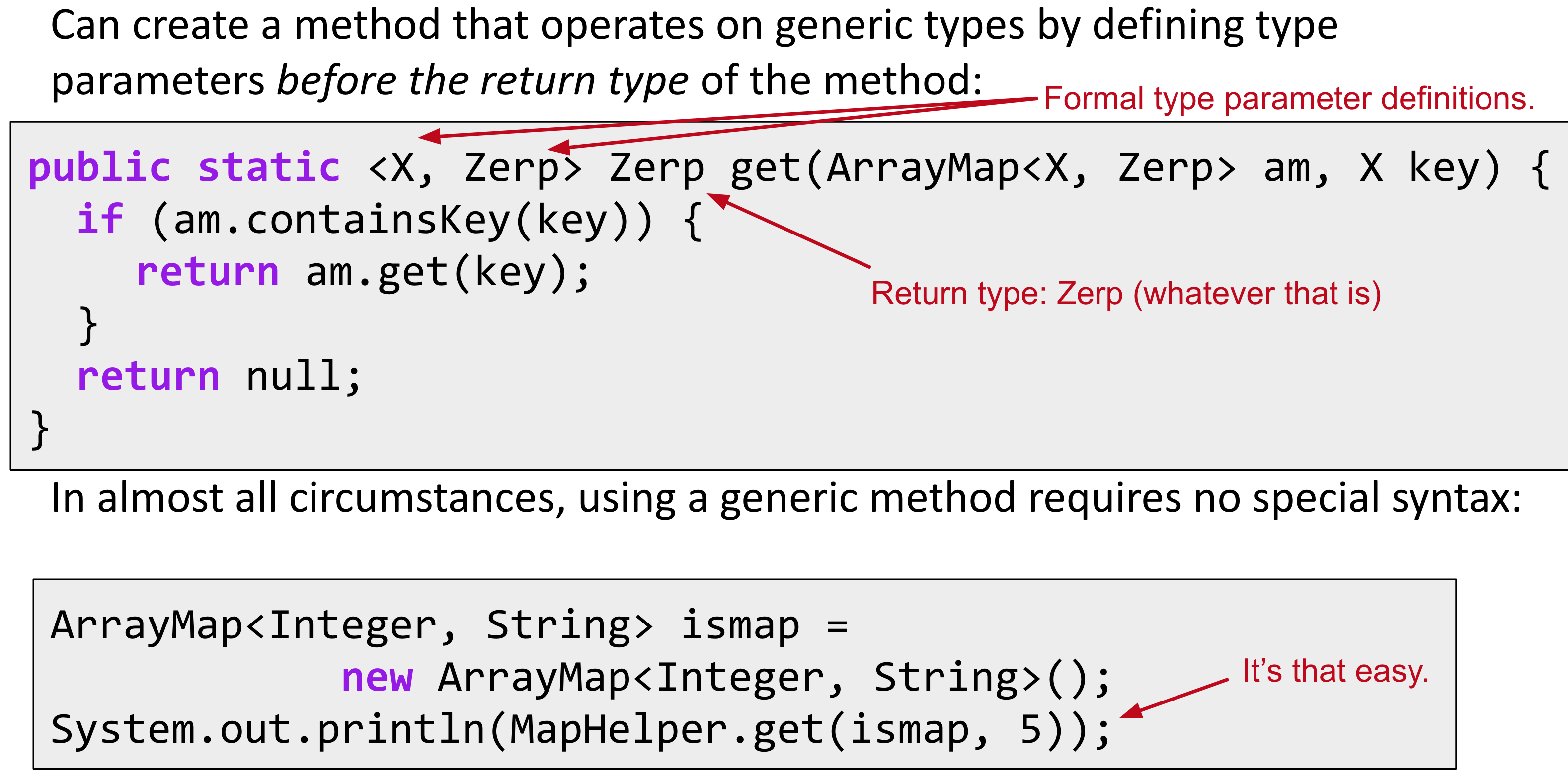
Create a class MapHelper with three methods:
- get(key): Returns the item in the map if it exists, otherwise null.
- maxKey(): Returns the maximum of all keys. Works only if keys can be compared.
- allBark(): Makes all keys bark. Works only for keys of type Dog.
Implement get():
Type Upperbound
Implement maxKey():
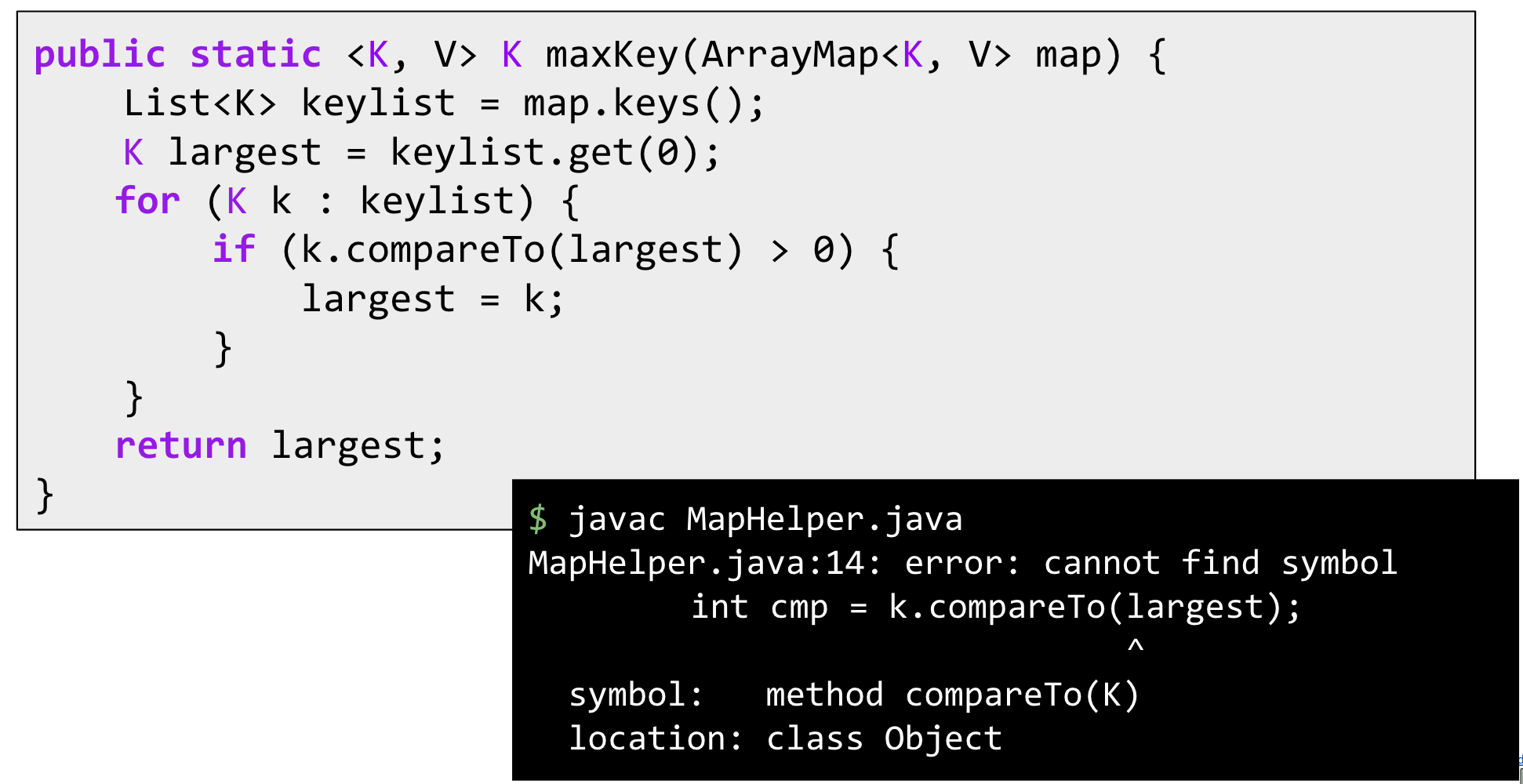
Can use extends keyword as a type upper bound. Only allow use on ArrayMaps with Comparable keys.
public static <K extends Comparable<K>, V> K maxKey(ArrayMap<K, V> am) {//Meaning: Any ArrayMap you give me must have actual parameter type that is a subtype of Comparable<T>.
...
if (k.compareTo(largest) > 0) {
...
}
Convariance
Implement allBark():
ArrayMap<FrenchDog, Integer> am2 = new ArrayMap<FrenchDog, Integer>();
am2.put(new FrenchDog("francis"), 10);
am2.put(new FrenchDog("francis jr"), 20);
allBark(am2);
//Method1: generic method
public static <V> void allBark(ArrayMap<Dog, V> am) {
for (Dog d : am.keys()) {
d.bark();
}
}
//Method2: WildCard
/*
public static void allBark(ArrayMap<Dog, ?> am) {
for (Dog d : am.keys()) {
d.bark();
}
}
*/
MapHelper.java:62: error: incompatible types: ArrayMap<FrenchDog,Integer> cannot be converted to ArrayMap<Dog,?>
Arrays are convariant in java, but generic types are invariant
反证: if 2(√),I made 3 without telling List, then 4(x) => 2(x)
Object[] numArray = new int[]{1,2,3}; // Correct
List<Dog> fg = new ArrayList<Dog>();
List<Animal> g = fg;
g.add(new Cat());
Dog s = g.get(0);
Fix
//正确
public static <K extends Dog> void allBark(ArrayMap<K, ?> am) {
for (Dog d : am.keys()) {
d.bark();
}
}
//or
public static void allBark(ArrayMap<?extends Dog,?> am){
for(Dog d : am.keys()){
d.bark();
}
}
Type Inference
Type inference is a Java compiler's ability to look at each method invocation and corresponding declaration to determine the type argument (or arguments) that make the invocation applicable.
Map<String, List<String>> myMap = new HashMap<>();// <String,List<String>>
class MyClass<X> {
<T> MyClass(T t) {
// ...
}
}
MyClass<Integer> myObject = new MyClass<>("");// X should be Integer, T should be String