7 DP
思路
(1)写状态方程
- 刷表法--考虑每个状态影响到的状态
- 只有当每个状态所依赖的状态对它的影响相互独立时才能用刷表法
- 填表法--考虑每个状态的依赖
(2)确定状态类型: has/remain情况下的最优subproblem
Eg: Knapsack
- has: 总体积不超过T的情况下最大重量dp[T]=dp[T-v[i]]+w[i]
- remain: 总体积实际剩余T时最大重量dp[T]=dp[T+v[i]]+w[i]
(3) Tabulation/ Memoization
- Tabulation: bottom up
- 确定Iteration顺序: 是否会被当前大循环条件下决策所影响
- 确定边界: 根据数组边界, 但记得额外处理
- Memoization: Top down Recursion
// Memoization solution of Fibonacci
int solve(int i){
if(dp[i] >= 0) return dp[i];
if(i==1 || i==2){
dp[i]=1;
}
else{
dp[i] = solve(i-1) + solve(i-2);
}
return dp[i];
}
最后的处理
求端点值 or 求min/max_element
涉及求字典序(或涉及dp的序号获取)
- 法1:去掉不可达结点,初始化为-inf(max)inf(min)
- 法2:加入实际has数组
Linear DP
Longest Consecutive Sequence
末尾来源连续
Longest Increasing Subsequence
Solution1: O()
LISEnding(n): length of longest increasing sub-sequence that ends in A[n]
LISEnding(i) = max(LISEnding(j) + 1, LISEnding(i)), A[j] < A[i]
Solution2: Since we do not care about particular LISEnding, we could use binary search to set dp[i]: the largest encoding number that forms i increasing subsequences.
for(int j=0;j<m;++j){
*lower_bound(dp,dp+m,x)=x;
}
变式: Perfect Squares
Given a positive integer n, find the least number of perfect square numbers (for example, 1, 4, 9, 16, ...) which sum are equal to n.
dp[i] = 1 +
Runtime: O(nlogn)
Longest Common Subsequence
末尾来源:交叉两种, 故加个空间保存上一行即可
Runtime: O(mn)
for(int i=0;i<strlen(a);++i){
for(int j=0;j<strlen(b);++j){
if(a[i]==b[j])dp[j]=(j-1<0?0:last[j-1])+1;
else dp[j]=max(j-1<0?0:dp[j-1],last[j]);
}
last=dp;
}
变式: Edit Distance
distance between strings = gaps + mismatches
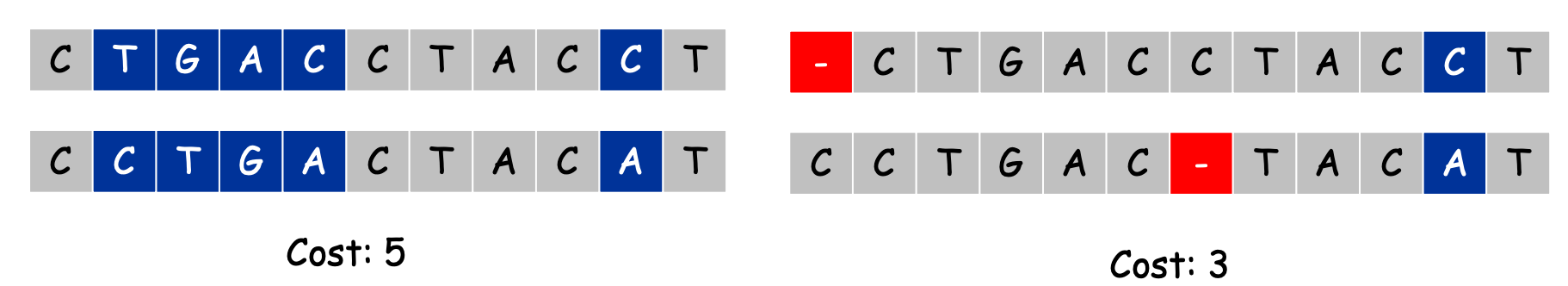
Given two strings, find an alignment with the minimum edit distance
dp[j] = min(xi!=yi + last[j-1],
1 + last[j], // gap in xi
1 + dp[j-1] // gap in yj
)
Knapsack
Unbounded knapsack problem
maximize subject to
Recursion方向: 考虑时, 要被当前影响
Runtime: O(mn)
for(int i=0;i<m;++i){
scanf("%d%d",&v,&p);
// has思路, 回溯为小, 故递增方向求dp[n]
for(int j=v;j<=n;++j)
dp[j]=max(dp[j],dp[j-v]+v*p);
// remain思路, 回溯为大,故递减方向求dp[0]
// for(int j=n-v;j>=0;--j)
// dp[j]=max(dp[j],dp[j+v]+v*p);
}
0-1 Knapsack
maximize subject to
Iteration方向: 考虑时, 不能被当前影响
Runtime: O(mn)
for(int i=0;i<m;++i){
scanf("%d%d",&v,&p);
// has思路, 回溯为小, 故递减求dp[n]
for(int j=n;j>=v;--j)
dp[j]=max(dp[j],dp[j-v]+v*p);
// remain思路, 回溯为大, 故递增求dp[0]
// for(int j=0;j<=n-v;++j)
// dp[j]=max(dp[j],dp[j+v]+v*p);
}
Longest Palindromic Subsequence
Given a string s, find the longest palindromic subsequence's length in s.
A subsequence is a sequence that can be derived from another sequence by deleting some or no elements without changing the order of the remaining elements.
区间型: 左右皆可变, 大循环考虑length, 小循环考虑端点
for(int i = 0 ;i < n;++i)dp[i][i] = 1; // length = 0
for(int j = 1;j < n;++j)
for(int i = 0;i + j < n; ++i){
dp[i][i + j] = max(dp[i][i + j],dp[i + 1][i + j], dp[i][i + j -1]);
if(a[i] == a[i + j]) dp[i][i+j] = max(dp[i][i+j],dp[i+1][i+j-1] + 2);
}
Tree DP
Minimum Vertex Cover
void dfs(vector<int> adj[], vector<int> dp[], int src){
for (auto child : adj[src]) {
// not including source in the vertex cover
dp[src][0] += dp[child][1];
// including source in the vertex cover
dp[src][1] += min(dp[child][1], dp[child][0]);
}
dp[src][1] += 1;
}
dfs(adj, dp, src);
result = min(dp[src][0], dp[src][1]);
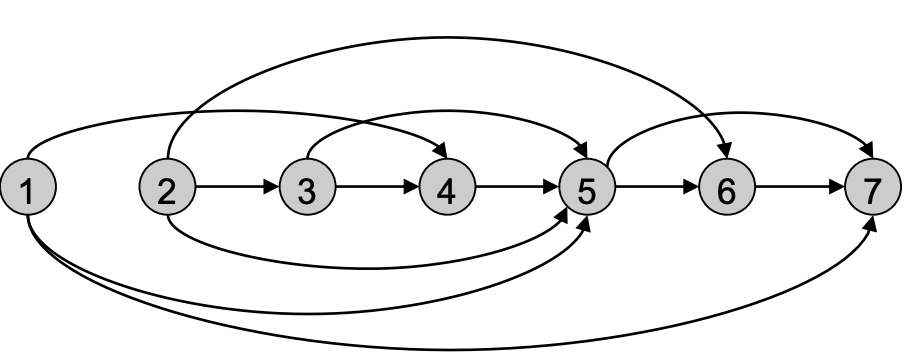
DAG
Suppose we have labelled the vertices such that (i,j) is a directed edge only if 𝑖 < 𝑗.
from the topological sort, we can define DP functions.
Tour
John Doe, a skilled pilot, enjoys traveling. While on vacation, he rents a small plane and starts visiting beautiful places. To save money, John must determine the shortest closed tour that connects his destinations. Each destination is represented by a point in the plane pi = <xi,yi>. John uses the following strategy: he starts from the leftmost point, then he goes strictly left to right to the rightmost point, and then he goes strictly right back to the starting point. It is known that the points have distinct x-coordinates.
Write a program that, given a set of n points in the plane, computes the shortest closed tour that connects the oints according to John's strategy.
最优子结构显然无法从rightmost点入手, 上下两条是互相平行不相交的折线-> 考虑某时刻上路停在i点, 下路停在j点, 可考虑max(i,j) = rightmost
不难发现dp[i][j] = dp[j][i], 为避免重复, 可以只考虑i > j的情况
这样考虑dp[i][j]上下路分别往rightmost走一步只会产生两种变化: dp[i + 1][j] 和 dp[i + 1][i](实际是dp[i][i + 1])
对于状态方程也有两种思路
- 刷表法: 建立has, i = 0:n - 1, j = 0: i, 但要注意的是dp[i][i]在i = 0时可以存在,需单独处理
- 填表法: 建立remain, 这样只需要一个方程, iteration顺序得是n-1: 0, 另外i = n-1 时需要单独处理
int solution1(){// 刷表法
dp[1][0] = d(0,1);
for(int i = 0;i< n-1;++i)for(int j =0 ;j<i;++j){
dp[i + 1][j] = dp[i][j] + d(i, i + 1);
if(dp[i + 1][i] ==0) dp[i + 1][i] = dp[i][j] + d(j,i + 1);
else dp[i + 1][i] = min(dp[i + 1][i], dp[i][j] + d(j, i + 1);
}
printf("%.2f\n",dp[n-1][n-2]+d(n-2,n-1));
}
int solution2(){// 填表法
for(int i = n-1;i>=0;--i)for(int j =0 ;j<i;++j){
if(i == n-1)dp[i][j] = d(j,i);
else dp[i][j] = min(dp[i + 1][j] + d(i + 1,i),
dp[i +1][i] + d(j, i + 1)
);
}
printf("%.2f\n",dp[1][0]+d(0,1));
}